Table of contents
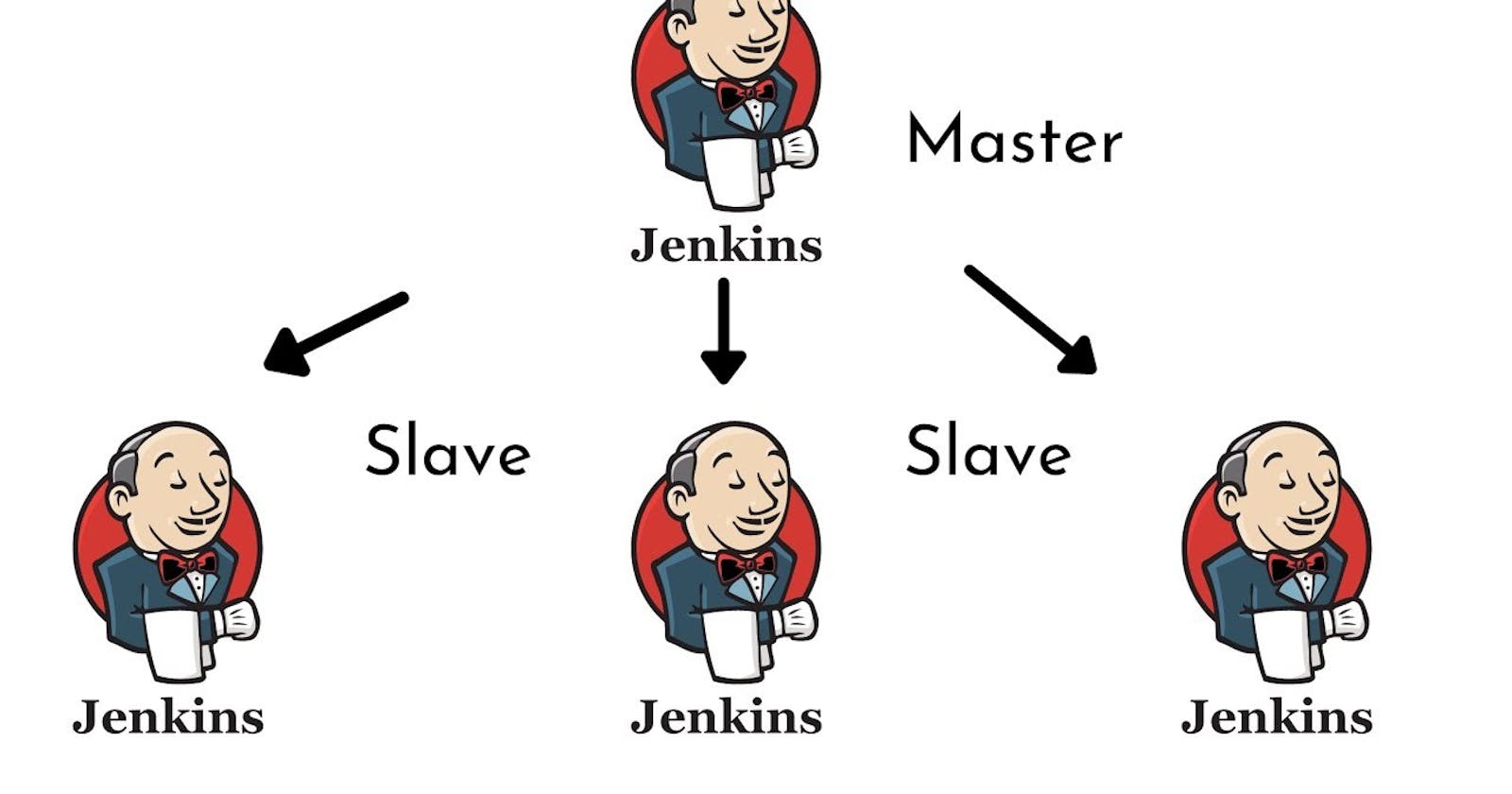
Jenkins Master (Server)
Jenkins’s server or master node holds all key configurations. The Jenkins master server is like a control server that orchestrates all the workflow defined in the pipelines. For example, scheduling a job, monitoring the jobs, etc.
Jenkins Agent
An agent is typically a machine or container that connects to a Jenkins master and this agent executes all the steps mentioned in a Job. When you create a Jenkins job, you have to assign an agent to it. Every agent has a label as a unique identifier.
When you trigger a Jenkins job from the master, the actual execution happens on the agent node that is configured in the job.
A single, monolithic Jenkins installation can work great for a small team with a relatively small number of projects. As your needs grow, however, it often becomes necessary to scale up. Jenkins provides a way to do this called “master to agent connection.” Instead of serving the Jenkins UI and running build jobs all on a single system, you can provide Jenkins with agents to handle the execution of jobs while the master serves the Jenkins UI and acts as a control node.

Pre-requisites
Let’s say we’re starting with a fresh Ubuntu 22.04 Linux installation. To get an agent working make sure you install Java ( same version as Jenkins master server ) and Docker on it.
Note:- While creating an agent, be sure to separate rights, permissions, and ownership for Jenkins users.
Task: 1
Create an agent by setting up a node on Jenkins
Create a new AWS EC2 Instance and connect it to the master (Where Jenkins is installed)
The connection of the master and agent requires SSH and the public-private key pair exchange.
Verify its status under the "Nodes" section.
Step: 1
Create two EC2 instances one for the master and the other one for the agent.

Step: 2
Generate SSH keys on Jenkins-master EC2 instance (ssh-keygen -t ed25519)

Step: 3
Add public key from Jenkins-master instance to Jenkins-agent instance under location .ssh/authorized_keys

Step: 4
Try to connect Jenkins-agent from Jenkins-master

Step: 5
Install Java on the Jenkins-agent installation link

Step: 6
Create an agent by setting up a node on Jenkins
Go to the Jenkins dashboard, and click on Manage Jenkins --> Set up agent


Select the launch method as Launch agents via SSH Give the public IP of the agent in the host field.

Click on Add under Credentials.

Add the private key that we created in a Jenkins-master instance using ssh-keygen

Below we select Ubuntu for credentials

Click on save which will create a node.

Task: 2
Run your previous Jobs on the new agent
Use labels for the agent, your master server should trigger builds for the agent server.
Step: 1
Create a new job and give it to any name, select Pipeline and save.

Step: 2
Give a general description.

In the pipeline script set the dev-server as follows and click on save


on the console output we can see on pipeline running on the dev-server

📍 Conclusion :
In this blog, we cover Jenkins Agents & we saw how we can configure & run a Jenkins pipeline on an agent node. In the next blog, we will cover some of Jenkins's Important interview questions.
Thank you for reading!
Contact me on Linkedin 🤝
Check out my GitHub for more resources 📚